Transfer and Manage Phone Data on The PC
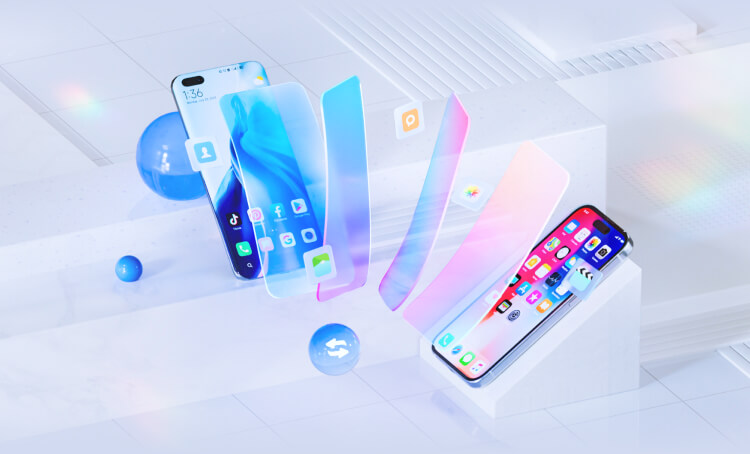
Transfer Your Phone Data Without A Computer
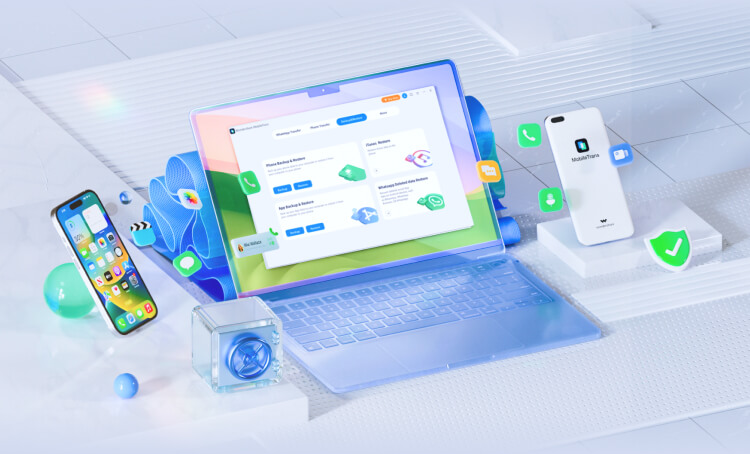
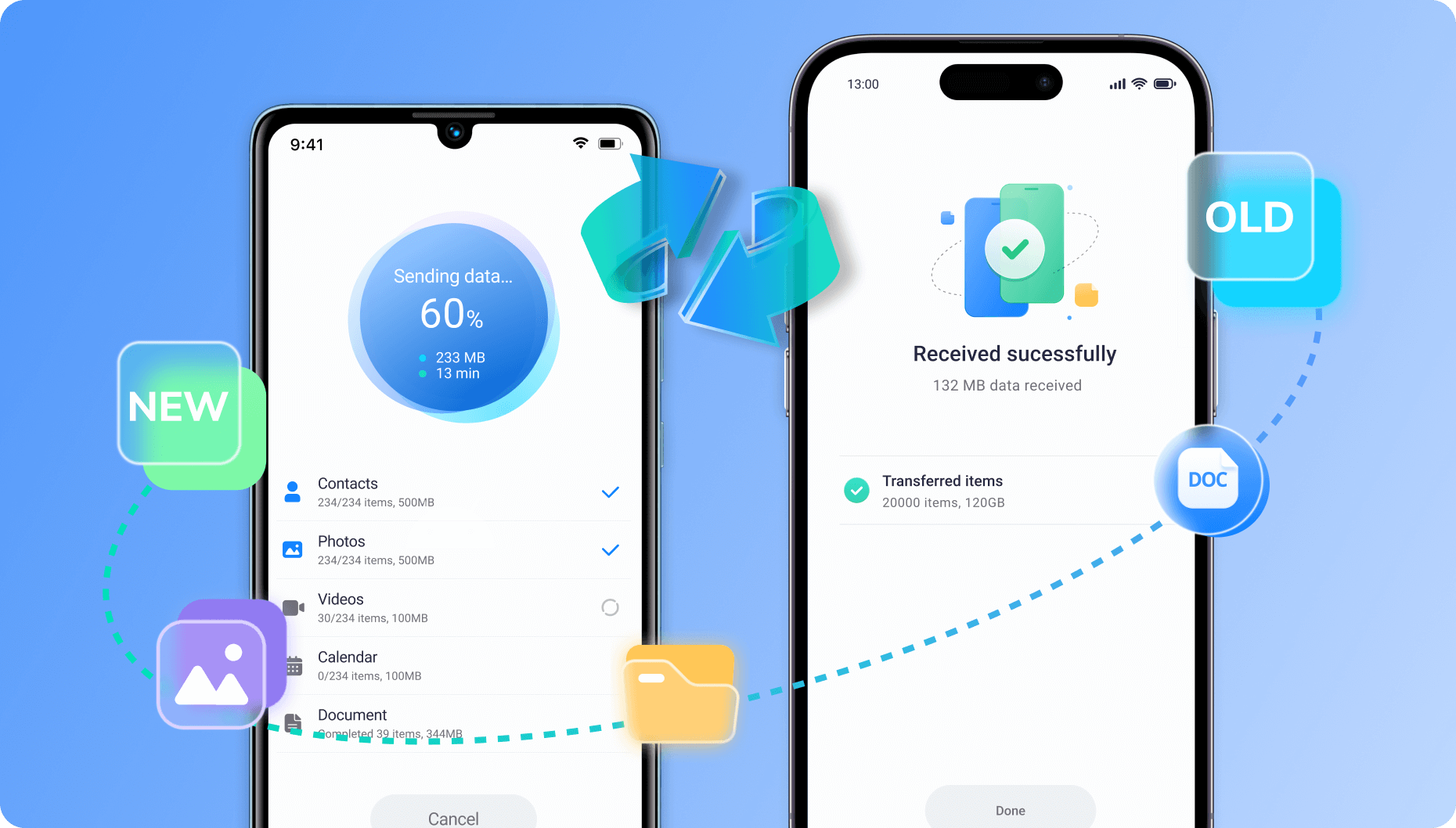
Phone Transfer App
Discover MobileTrans App, your go-to mobile transfer application for wirelessly transferring files remotely. Effortlessly move up to 10 phone data types without using cellular data or requiring cables. Enjoy fast, secure transfers at your convenience!
Learn More>>
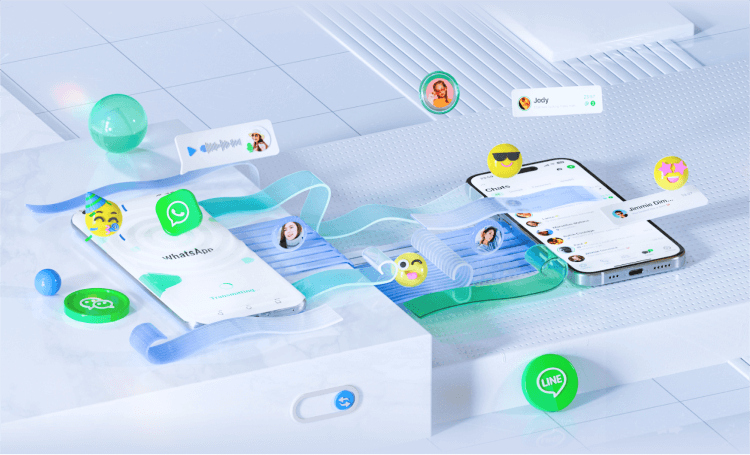
WhatsApp Transfer Wirelessly
Mutsapper simplifies transferring and merging multiple WhatsApp data types between Android and iPhone.
It supports WhatsApp, WhatsApp Business, and GBWhatsApp, allowing you to transfer chats and media easily. You can also migrate WhatsApp from Google Drive to iPhone, keeping your important conversations accessible!
Learn More>>
It supports WhatsApp, WhatsApp Business, and GBWhatsApp, allowing you to transfer chats and media easily. You can also migrate WhatsApp from Google Drive to iPhone, keeping your important conversations accessible!

More Features to Explore
 new
new

WhatsApp Last Seen Tracker
Track multi-contacts' WhatsApp activities easily. Get instant online/offline notifications and reveal their hidden status with WaLastseen.
Learn More>>

Music Playlist Transfer
Transfer playlists from one streaming service to another, supporting Apple Music, Spotify,
YouTube Music and More.
Learn More>>
YouTube Music and More.

Contact Management
Effortlessly manage and merge duplicate contacts while converting contact formats for seamless organization.
Learn More>>

HEIC Converter
Convert multiple HEIC photos to JPG format effortlessly while preserving the image quality for stunning results.
Learn More>>
Why Choose Wondershare MobileTrans?
+
File Formats
+
Devices
%+
Privacy Protection
Hour